Balance Training
Balance Training Physical Therapy in Manhattan is one of the most highly structured balance programs for all functional levels.
When talking about the fall risks, balance training is the first thing that comes into mind. Balance is a ubiquitous force that keeps everything moving along its course, from planets to living organisms. Those are the physical and biophysical forces that promote and sustain life. In this article I will be talking about the physical balance which sustains our equilibrium and promotes our optimal functioning lifestyle.
Systematic Balance Training
As a long time physical therapist at Gramercy Physical Therapy (www.gptny.com), I put practicality and quality at the forefront of my practice. I was always determined to improve my patients’ balance and enable them to succeed. From working with athletes to patients who have suffered a stroke, I continued to have the same conclusion— a systematically structured balance training program improves functional balance; a system I call SBT (Systematic Balance Training.)
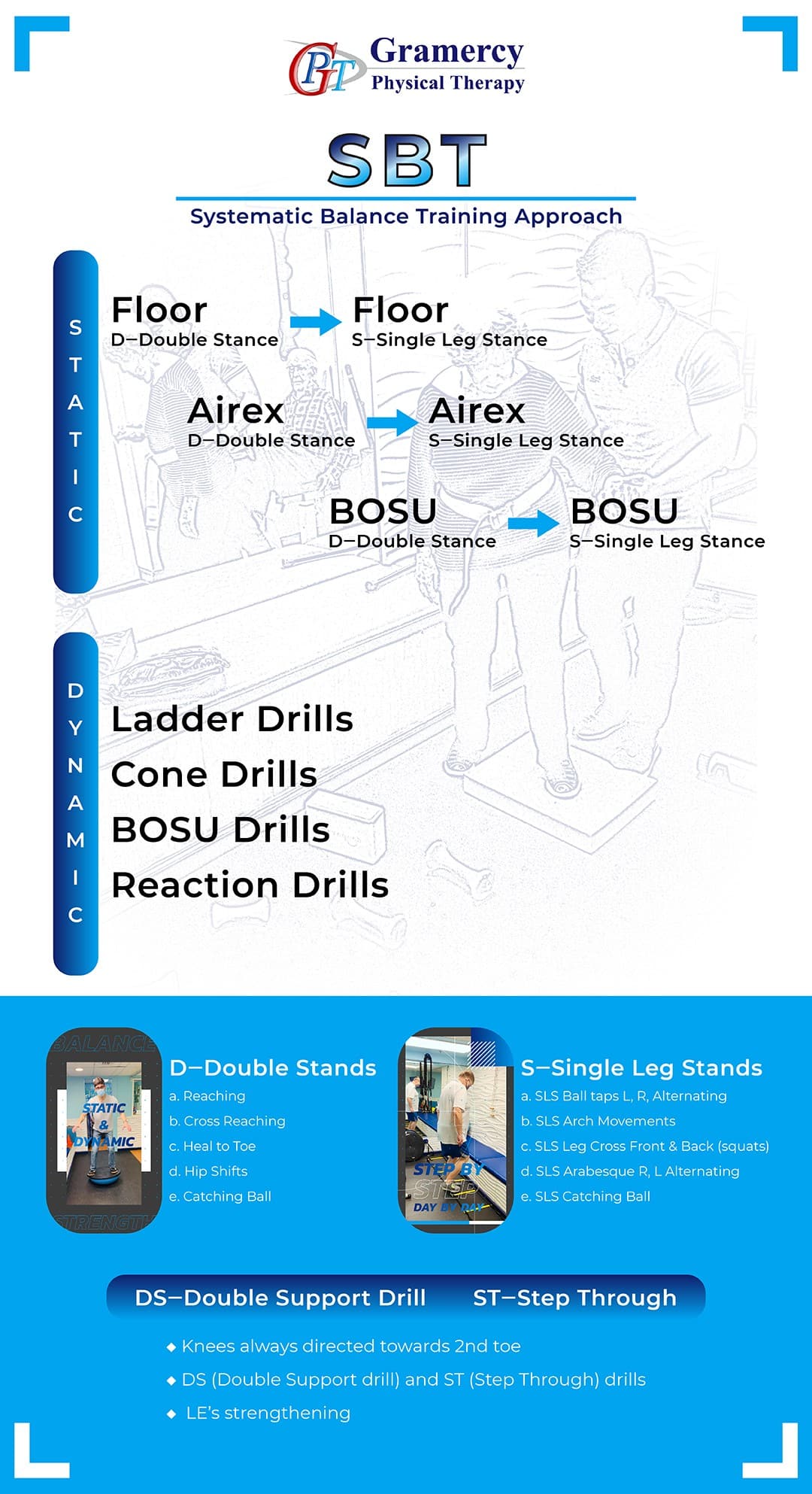
The SBT approach includes two main elements: 1. A systematic list of supervised balance drills with proper progression. Why supervised? The balance drills are designed to compromise your balance to some degree in order to challenge your proprioceptive system and push your barriers to new limits. For some, training balance alone is less effective and poses risk and potential harm. 2. Mobility exercises, strengthening and tissue flexibility are crucial to allow the necessary movement that sustains equilibrium and maintain the patient’s center of mass within their base of support.
Impairment in balance can have various etiologies so it is important to recognize its root origin to implement the most effective treatment. A few common conditions that may affect balance include: Impaired proprioception, physical injury, immobility, immobilization, apprehension, joint or muscle pain, inner ear dysfunction, brain trauma, vestibular dysfunction, etc. Conditions deriving from the inner ear and vestibular system will benefit from vestibular therapy, while the rest can be treated using the SBT approach.
In the study published by the Journal of Geriatric Physical Therapy, “Determining Risk of Falls in Community Dwelling Older Adults: A systematic Review and Meta-analysis Using Posttest Probability”, works to determine clinically useful indicators of risk of future falls. The study breaks down into 3 categories of Medical history questions, Self report measures, and Performance-based functional measures. The study concludes that for the medical history questions category, any previous falls shown to have a low to moderate predictability for future falls. The Self-report measures category found a low to moderate predictability based of Geriatric depression scale. Finally, the performance based functional measure category showed that the Berg Balance Scale shown to have a moderate predictability of future falls.
For conclusion, anyone with a history of falls should seek balance physical therapy training due to the low to moderate falls predictability. On the side of the physical therapist, the Berg test and the TUG test are shown to provide moderate predictability insight for falls.

